What Should You Know About Skin Cancer? Signs, Prevention, and Treatment
Table of Contents
What Should You Know About Skin Cancer? Signs, Prevention, and Treatment
Introduction
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer globally, with millions of new cases diagnosed each year. Yet, many people underestimate its seriousness or think it can’t happen to them. The reality is that skin cancer can affect anyone, regardless of skin type or age.
Understanding skin cancer, including its warning signs, prevention methods, and treatment options, is crucial for protecting yourself and your loved ones. This guide will break down everything you need to know, from recognizing early symptoms to adopting preventive measures like sun protection and regular skin checks.
If you’ve ever wondered how something as simple as sunlight could lead to a life-threatening condition, this blog will give you the answers you need.
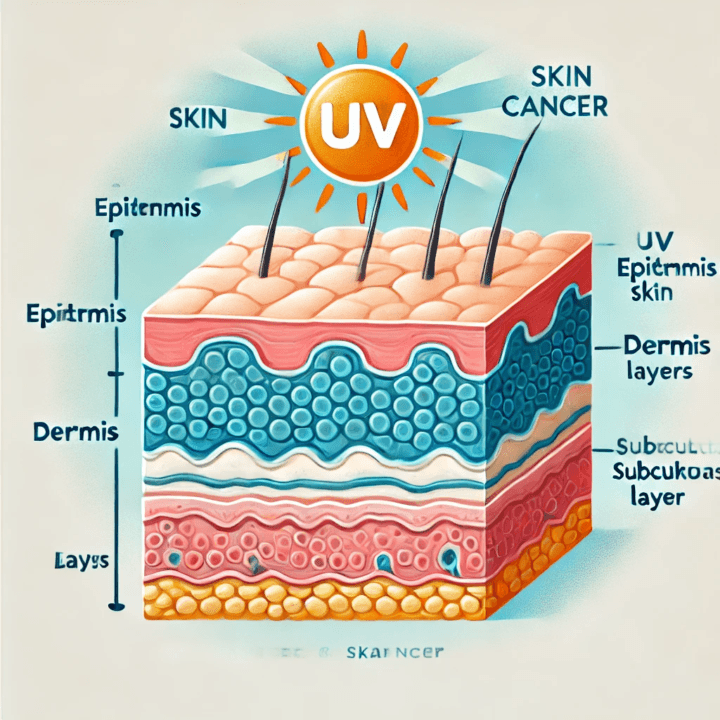
What Is Skin Cancer and How Does It Develop?
Skin cancer occurs when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably due to DNA damage, often caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. There are several types of skin cancer, but the most common include:
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
- Most common type of skin cancer.
- Origin: Develops in the basal cells found in the outermost skin layer.
- Appearance: May look like a waxy bump, pink patch, or open sore.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
- Second most common type of skin cancer.
- Origin: Develops in the squamous cells, which make up the middle and outer layers of the skin.
- Appearance: May appear as scaly patches, open sores, or warts.
3. Melanoma (Most Dangerous)
- Rarest but deadliest form of skin cancer.
- Origin: Starts in the melanocytes, which produce melanin (skin pigment).
- Appearance: Often resembles a mole that changes shape, size, or color.
What Are the Warning Signs of Skin Cancer?
Early detection is key, and knowing what to look for can save your life.
The ABCDE Rule for Melanoma
- A – Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn’t match the other half.
- B – Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined borders.
- C – Color: Varying shades of brown, black, or even red, white, or blue.
- D – Diameter: Larger than 6 mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- E – Evolving: Any change in size, shape, or symptoms like bleeding or itching.
Other Signs to Watch For
- Sores that don’t heal.
- Red, scaly patches that persist.
- Waxy or shiny bumps.
- Painful or bleeding spots.
How Can You Prevent Skin Cancer?
While not all cases are preventable, taking these proactive steps can greatly reduce your risk:
1. Wear Sunscreen Daily
- Why: UV exposure is the leading cause of skin cancer.
- What to use: Broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30.
- Tip: Reapply every two hours, especially if swimming or sweating.
2. Limit Sun Exposure During Peak Hours
- The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 AM and 4 PM.
- Wear protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses.
3. Avoid Tanning Beds
- Artificial UV radiation is just as harmful as natural sunlight.
- Regular use of tanning beds significantly increases the risk of melanoma.
4. Conduct Regular Skin Exams
- Perform self-examinations monthly.
- Look for new or changing moles, sores, or lesions.
- Schedule annual dermatologist visits for professional checks.
What Are the Treatment Options for Skin Cancer?
The type and stage of skin cancer will determine the treatment approach:
1. Surgical Removal
- Description: A dermatologist or surgeon removes the cancerous lesion and surrounding tissue.
- Effective for: Most BCCs, SCCs, and some early-stage melanomas.
2. Mohs Surgery
- Description: Layers of skin are removed and examined until only cancer-free tissue remains.
- Effective for: High-risk areas like the face and recurrent skin cancers.
3. Radiation Therapy
- Description: Uses targeted radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Effective for: Larger or difficult-to-operate tumors.
4. Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
- Description: Boosts the immune system or targets specific cancer cells.
- Effective for: Advanced melanomas or cases where surgery isn’t possible.
How Can Skin Cancer Affect You Emotionally and Mentally?
Beyond the physical impact, a skin cancer diagnosis can cause emotional stress, anxiety, and fear of recurrence. It’s important to seek support, whether through counseling, support groups, or family and friends. Early detection and a positive mindset can significantly improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Skin cancer is a serious but largely preventable disease. By understanding its causes, recognizing warning signs, and taking proactive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk. Early detection is your best defense, so make skin checks a regular part of your self-care routine. Remember, protecting your skin today means a healthier future. Stay safe, stay informed, and always wear sunscreen!
FAQ
1. Can skin cancer be cured?
Yes, when caught early, most cases of skin cancer are highly treatable. Melanoma is more dangerous but can be cured if detected in the early stages.
2. Is sunscreen enough to prevent skin cancer?
Sunscreen is a critical part of prevention, but it should be combined with protective clothing, limited sun exposure, and regular skin exams.
3. Can dark-skinned individuals get skin cancer?
Yes, while the risk is lower, dark-skinned individuals can still develop skin cancer. Melanoma in these cases often appears on non-sun-exposed areas.
4. Are all moles dangerous?
No, most moles are harmless, but any mole that changes in size, shape, or color should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
5. Does diet play a role in skin cancer prevention?
A healthy diet rich in antioxidants can help reduce skin damage, but it should complement—not replace—physical sun protection.












Post Comment