Top 15 Headache Triggers: Identify and Avoid Your Pain Culprits
Table of Contents
As someone who has grappled with headaches for years, both personally and professionally, I’ve come to understand the profound impact that identifying and managing triggers can have on one’s quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the top 15 headache triggers that I’ve encountered in my research and clinical experience. By understanding these common culprits, you’ll be better equipped to recognize and mitigate your personal headache triggers.
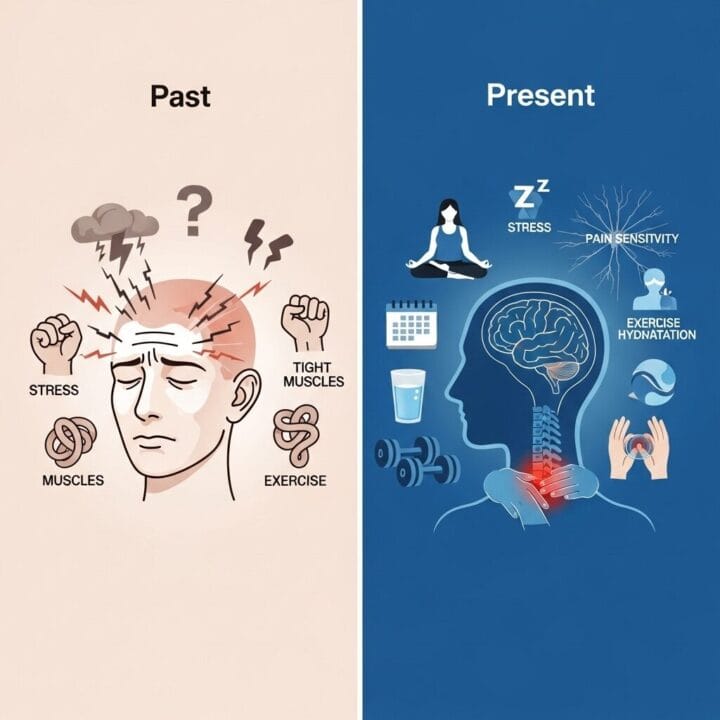
1. Stress: The Universal Trigger
Stress is perhaps the most ubiquitous headache trigger, affecting individuals across all demographics. The physiological changes induced by stress, including increased muscle tension and altered neurotransmitter levels, can precipitate various types of headaches. Implementing stress management techniques such as mindfulness meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, or cognitive-behavioral therapy can be instrumental in reducing stress-related headaches.
2. Sleep Disturbances: A Delicate Balance
Both insufficient and excessive sleep can trigger headaches. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and practicing good sleep hygiene are crucial. This includes creating a relaxing bedtime routine, optimizing your sleep environment, and addressing any underlying sleep disorders such as sleep apnea.
3. Dietary Factors: The Food-Headache Connection
Certain foods and beverages are known headache triggers for many individuals. Common culprits include:
- Aged cheeses
- Processed meats containing nitrates
- Chocolate
- Artificial sweeteners
- Monosodium glutamate (MSG)
Keeping a food diary can help you identify your personal dietary triggers.
4. Caffeine: A Double-Edged Sword
While caffeine can alleviate some headaches, it can also trigger them, especially when consumed in excess or during withdrawal. Moderation is key, and it’s advisable to maintain consistent caffeine intake or gradually reduce consumption if you’re trying to cut back.
5. Dehydration: The Often Overlooked Trigger
Inadequate fluid intake can lead to dehydration, a common headache trigger. Ensure you’re consuming sufficient water throughout the day, particularly in hot weather or during physical activity.
6. Hormonal Fluctuations: The Gender-Specific Trigger
For many women, hormonal changes associated with menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can trigger headaches. Working with a healthcare provider to manage hormonal imbalances can be beneficial in these cases.
7. Environmental Factors: The Sensory Overload
Bright lights, loud noises, and strong odors can all trigger headaches in sensitive individuals. Identifying and minimizing exposure to these environmental stimuli can help prevent headaches.
8. Weather Changes: The Atmospheric Influence
Barometric pressure changes, temperature fluctuations, and humidity levels can all impact headache frequency. While we can’t control the weather, being aware of these triggers can help you prepare and take preventive measures.
9. Physical Exertion: The Exercise Paradox
While regular exercise can help prevent headaches, intense physical activity can sometimes trigger them. Gradual warm-ups and proper hydration can help mitigate exercise-induced headaches.
10. Posture and Ergonomics: The Modern-Day Trigger
Poor posture, especially during prolonged periods of desk work or smartphone use, can lead to tension headaches. Implementing ergonomic improvements and taking regular breaks to stretch can be highly beneficial.
11. Medication Overuse: The Rebound Effect
Ironically, overuse of pain medications can lead to rebound headaches. It’s crucial to use pain relievers judiciously and under medical guidance to avoid this paradoxical effect.
12. Alcohol: The Social Lubricant with a Downside
Alcoholic beverages, particularly red wine, can trigger headaches in susceptible individuals. This may be due to compounds like histamines and sulfites present in these drinks.
13. Eyestrain: The Digital Age Dilemma
Prolonged screen time can lead to eyestrain and subsequent headaches. Implementing the 20-20-20 rule (every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds) and ensuring proper lighting can help reduce this trigger.
14. Hunger and Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Skipping meals or experiencing rapid changes in blood sugar levels can trigger headaches. Maintaining regular meal times and balanced blood sugar levels through proper nutrition is important.
15. Underlying Medical Conditions
Sometimes, headaches can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions such as sinusitis, hypertension, or temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders. Addressing these underlying issues with appropriate medical care is crucial for long-term headache management.
Conclusion: Empowerment Through Knowledge
Understanding your personal headache triggers is a powerful step towards effective management. By systematically identifying and addressing these triggers, many individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of their headaches. However, it’s important to remember that headache management is often multifaceted and may require a combination of lifestyle modifications, preventive strategies, and, in some cases, medical interventions.
If you find that your headaches are frequent, severe, or significantly impacting your quality of life, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, help identify any underlying causes, and develop a tailored treatment plan to address your specific needs.
Remember, the journey to better headache management is often one of continuous learning and adaptation. Be patient with yourself, stay observant of your triggers, and don’t hesitate to seek support when needed. With persistence and the right strategies, you can gain greater control over your headaches and improve your overall well-being.









Post Comment