Is Your Ear Pain Actually TMJ? Unraveling the TMJ-Ear Infection Connection Symptoms
Table of Contents
Is Your Ear Pain Actually TMJ? Unraveling the TMJ-Ear Infection Connection Symptoms
Introduction
Are you constantly battling earaches—nagging pain that just won’t quit? Maybe you’ve seen a doctor, ruled out an actual ear infection, and yet, the discomfort lingers. Or perhaps you’re dealing with jaw pain, clicking, or popping noises when you chew, and you didn’t even consider it could be linked to your ear issues. If so, you’re not alone.
Many people experience what seems like ear infection symptoms, but the real culprit might be your temporomandibular joint (TMJ). The connection between TMJ and ear pain, often misdiagnosed as an ear infection, is a complex issue that leaves many scratching their heads. The question isn’t just “Do I have an ear infection?” it’s “Could my jaw be causing this?”
This guide will dive deep into the TMJ-ear infection connection symptoms, helping you understand the link, identify the signs, and finally, take steps towards finding relief. We will break down the complexities in an easy-to-understand way, using straightforward language. It’s time to get clarity and discover what could be behind your ear pain.
Decoding the TMJ-Ear Connection: It’s More Than You Think
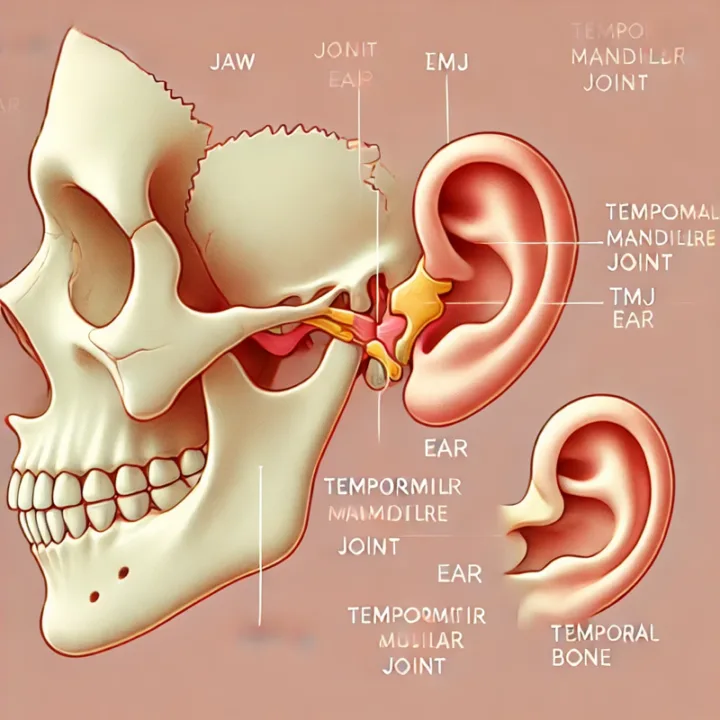
You might be thinking, “Wait, my jaw is connected to my ear? How?” The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is essentially a hinge that connects your jawbone to your skull, located right in front of your ears. This intricate joint allows you to chew, speak, and yawn. When this joint isn’t functioning correctly, it can cause a cascade of issues, including symptoms that mimic an ear infection.
Think of it like this: imagine a door hinge that’s misaligned. The door might rub against the frame, causing friction and odd noises. Similarly, when your TMJ isn’t aligned properly, it can cause inflammation and muscle tension which can radiate pain to the surrounding areas, including your ear. The nerves that send signals from the TMJ are closely connected to the nerves in your ear, explaining why TMJ problems often manifest as ear-related symptoms.
Common TMJ-Related Ear Symptoms: Are You Experiencing These?
It’s not always a straightforward earache, which is part of the reason why TMJ is frequently misdiagnosed. Common symptoms associated with TMJ include:
- Ear pain: A dull ache, sometimes a feeling of pressure, or even deep discomfort in the ear.
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears): Persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds.
- Vertigo (dizziness): Feelings of dizziness, lightheadedness, or imbalance.
- Ear fullness: A sensation that your ear is blocked even without fluid build-up.
- Reduced hearing or muffled sounds: Feeling like you’re hearing through cotton wool.
- Jaw pain and tenderness: Discomfort around your TMJ, temples, and surrounding muscles.
What Causes TMJ Disorders and Mimic Ear Infections?
Several factors contribute to TMJ issues that may lead to symptoms resembling an ear infection:
- Teeth Grinding (Bruxism): Constant grinding can stress the TMJ joint.
- Misaligned Bite (Malocclusion): Incorrect alignment causes strain.
- Stress: Increases muscle tension around the jaw and neck.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis can inflame the TMJ.
- Injury: Trauma to the jaw can lead to TMJ dysfunction.
- Poor Posture: Forward head posture puts stress on the jaw and neck muscles.
Identifying your specific triggers is crucial to addressing the TMJ issues causing your ear pain.
How to Differentiate TMJ from an Ear Infection
Distinguishing between TMJ and an actual ear infection is crucial. Consider the following:
- Primary Symptoms: Ear infections typically involve sharp pain, fever, and discharge; TMJ involves dull ache, jaw pain, and clicking.
- Recent History: Upper respiratory infections lean toward ear infections; stress and jaw pain suggest TMJ.
- Response to Treatment: If antibiotics don’t work, it may be TMJ.
Consulting a professional for an exam and imaging tests can provide clarity.
Effective Treatments for TMJ-Related Ear Symptoms
If you suspect TMJ-related ear pain, consider these treatment options:
- Home Remedies:
- Warm or cold compresses.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Gentle jaw exercises.
- Dental Interventions:
- Custom mouthguards to prevent grinding.
- Orthodontic treatments to correct bite issues.
- Physical Therapy:
- Exercises to improve jaw movement and posture.
- Medical Treatments:
- Muscle relaxants or anti-inflammatory medications.
Seeking professional help is essential in determining the best course of action.
Conclusion
Understanding the TMJ-ear connection can be challenging, but recognizing the signs and getting appropriate treatment is key to finding relief. Whether through lifestyle changes, professional treatments, or a combination, addressing TMJ-related ear symptoms can significantly improve your quality of life.
FAQ
Q1: Can TMJ cause a feeling like my ear is clogged?
Yes, TMJ disorders can create a sensation of fullness or congestion in the ear.
Q2: If I don’t have jaw pain, can I still have TMJ-related ear symptoms?
Yes, TMJ can present as ear symptoms alone without jaw discomfort.
Q3: How can I tell if my ear symptoms are from TMJ or an infection?
Ear infections often involve fever and discharge, while TMJ symptoms include jaw pain and clicking.
Helpful Resources
For further reading, check out these helpful resources:










Post Comment