TMJ During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Safe Treatments
Table of Contents

Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders can be particularly challenging during pregnancy, a time when many women experience various physical discomforts. TMJ pain while pregnant is not uncommon, as hormonal changes and increased stress can exacerbate existing conditions or trigger new symptoms. This comprehensive guide explores the causes, symptoms, and safe treatment options for managing TMJ during pregnancy, helping expectant mothers find relief without compromising their health or that of their developing baby.
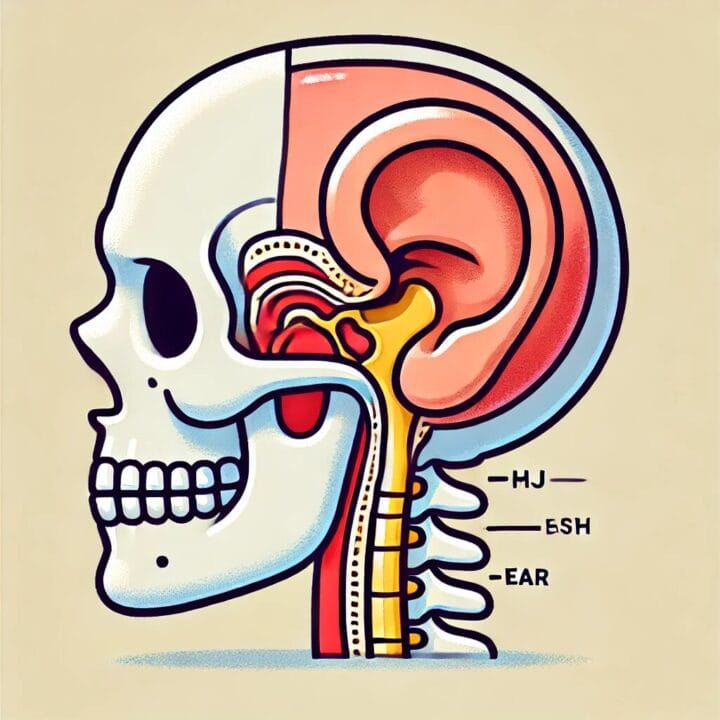
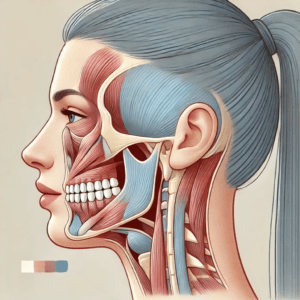
Understanding TMJ Disorders During Pregnancy
Temporomandibular joint disorders affect the jaw joint and surrounding muscles, causing pain and discomfort. During pregnancy, several factors can contribute to the onset or worsening of TMJ symptoms:
- Hormonal changes: Increased levels of relaxin and estrogen can affect joint stability.
- Stress and anxiety: Common during pregnancy, these can lead to teeth grinding and jaw clenching.
- Poor posture: As the body changes, posture adjustments can affect jaw alignment.
- Fluid retention: Swelling in facial tissues can put pressure on the jaw joint.
Understanding these factors is crucial for managing TMJ effectively during pregnancy.
Common Symptoms of TMJ While Pregnant
Recognizing TMJ symptoms during pregnancy is the first step towards finding relief. Common signs include:
- Jaw pain or tenderness
- Clicking or popping sounds when opening or closing the mouth
- Difficulty or discomfort while chewing
- Facial pain, particularly around the ear area
- Headaches, often resembling tension headaches
- Limited jaw movement or locking
These symptoms may vary in intensity and can be exacerbated by pregnancy-related factors.
Safe Treatment Options for TMJ During Pregnancy
Managing TMJ while pregnant requires careful consideration of treatment options that are safe for both mother and baby. Here are some effective and pregnancy-safe approaches:
1. Gentle Jaw Exercises
Performing gentle jaw exercises can help improve mobility and reduce pain:
- Slowly open and close your mouth
- Move your jaw side to side
- Practice controlled forward and backward movements
These exercises should be done carefully to avoid overexertion.
2. Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying warm compresses or ice packs to the jaw area can provide relief:
- Use for 10-15 minutes at a time
- Alternate between heat and cold for optimal results
- Always wrap the compress in a thin towel to protect your skin
3. Stress Management Techniques
Reducing stress can significantly alleviate TMJ symptoms:
- Practice prenatal yoga or gentle stretching
- Try meditation or deep breathing exercises
- Engage in relaxing activities like prenatal massage (with your doctor’s approval)
4. Dietary Modifications
Adjusting your diet can help reduce strain on the jaw:
- Opt for softer foods that require less chewing
- Cut food into smaller pieces
- Avoid chewy or tough foods that may aggravate symptoms
5. Proper Sleep Posture
Maintaining good sleep posture can prevent additional strain on the jaw:
- Sleep on your side with a pregnancy pillow for support
- Use a thin pillow to keep your head and neck aligned
6. Gentle Massage
Self-massage or professional massage therapy can help relax jaw muscles:
- Gently massage the jaw, temple, and neck areas
- Consider seeking a prenatal massage therapist experienced in TMJ relief
When to Seek Professional Help
While many TMJ symptoms can be managed at home, it’s important to know when to consult a healthcare provider:
- If pain is severe or persistent
- If you experience difficulty opening or closing your mouth
- If symptoms interfere with eating or speaking
- If you develop new or worsening symptoms
Your healthcare provider can offer additional treatment options and ensure that your symptoms are not indicative of other health concerns.
Long-term Management and Postpartum Care
Managing TMJ during pregnancy is often just the beginning. Consider these long-term strategies:
- Continue with beneficial lifestyle changes postpartum
- Monitor symptoms and seek follow-up care if needed
- Discuss potential treatments that were not suitable during pregnancy with your healthcare provider
Conclusion
TMJ disorders during pregnancy can be challenging, but with the right approach, symptoms can be effectively managed. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms early, and implementing safe treatment strategies, expectant mothers can find relief from TMJ pain while ensuring the health and well-being of their developing baby. Remember, every pregnancy is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment regimen, especially during pregnancy. With patience and proper care, you can navigate TMJ symptoms and focus on the joyous journey of pregnancy.
FAQs
- Q: Can TMJ develop for the first time during pregnancy?
A: Yes, hormonal changes and increased stress during pregnancy can trigger TMJ symptoms in some women who have never experienced them before. - Q: Are there any medications safe for treating TMJ during pregnancy?
A: Always consult your healthcare provider before taking any medication. Some over-the-counter pain relievers may be safe, but it’s crucial to get professional advice. - Q: Can TMJ affect my baby’s development?
A: TMJ itself does not directly affect fetal development. However, severe pain or stress can impact overall maternal well-being, which is why managing symptoms is important. - Q: Will my TMJ symptoms go away after pregnancy?
A: For some women, TMJ symptoms improve postpartum as hormone levels stabilize. However, others may need ongoing management. - Q: Can I use a night guard for TMJ while pregnant?
A: Night guards can be safe during pregnancy, but it’s best to consult with your dentist or healthcare provider to ensure it’s appropriate for your specific situation. - Q: How can I differentiate between TMJ pain and other pregnancy-related discomforts?
A: TMJ pain is typically localized to the jaw area and may be accompanied by clicking or popping sounds. If you’re unsure, consult your healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis. - Q: Are there any prenatal vitamins that can help with TMJ symptoms?
A: While no specific prenatal vitamins target TMJ symptoms, maintaining overall nutritional health during pregnancy is important. Discuss your nutritional needs with your healthcare provider.
Author Bio:
Dr. Emily Johnson, DDS, is a board-certified dentist specializing in orofacial pain and temporomandibular disorders. With over 15 years of clinical experience and a focus on women’s health, Dr. Johnson has published numerous articles on managing TMJ disorders during pregnancy. She is committed to providing comprehensive, patient-centered care and educating expectant mothers on safe and effective TMJ management strategies.
References:
Bayramova, A. (2018). TMD and pregnancy? Clinical Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1, 001-006. https://doi.org/10.29328/journal.cjog.1001001
Rakhshan, V., & Pakkhesal, M. (2020). Effects of pregnancy on temporomandibular joint and related structures: A systematic review. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, 47(7), 898-909. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.12962
Silveira, R. C. D., Selaimen, C. M. P., Brito, C. D. L., Grossi, M. L., & Grossi, P. K. (2007). Pregnancy and temporomandibular disorders: A review. Journal of Oral Science, 49(4), 265-269. https://doi.org/10.2334/josnusd.49.265
LeResche, L., Sherman, J. J., Huggins, K., Saunders, K., Mancl, L. A., Lentz, G., & Dworkin, S. F. (2005). Musculoskeletal orofacial pain and other signs and symptoms of temporomandibular disorders during pregnancy: A prospective study. Journal of Orofacial Pain, 19(3), 193-201.
Klopper, A. E., Deanne, R. B., & Watkins, L. R. (2020). Temporomandibular disorders in pregnancy: A review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(11), 3588. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9113588
Citations:
[1] https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/tmj-pregnant
[2] https://www.osteohealthcalgary.com/tmj-disorder-pregnancy/
[3] https://kelleymingus.com/jaw-dropping-pregnancy/
[4] https://www.claritychirotrt.com/blog/jaw-pain-and-pregnancy
[5] https://www.rickardschiropractic.com/jaw-pain-problem-among-pregnant-women/
[6] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41582-021-00509-5
[7] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560787/
[8] https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/physrev.00034.2015











Post Comment