How Are Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Connected to Ear Pain?
Table of Contents
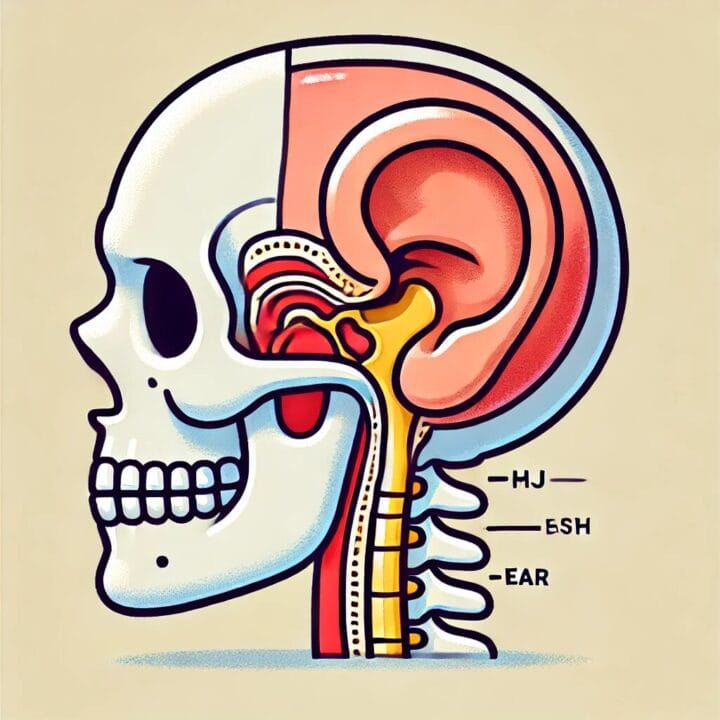
How Are Temporomandibular Joint Disorders Connected to Ear Pain? 🤔
Experiencing ear pain without an apparent ear infection can be perplexing. Interestingly, the culprit might be the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which plays a pivotal role in jaw movement. Let’s delve into how TMJ disorders can lead to ear discomfort and explore potential remedies.
What Is the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)? 🦷
The temporomandibular joint connects your jawbone to your skull, facilitating movements like chewing and speaking. Positioned near the ear canal, any dysfunction in this joint can manifest as ear-related symptoms.
How Do TMJ Disorders Cause Ear Pain? 🎯
TMJ disorders (TMD) can lead to ear pain through several mechanisms:
- Inflammation Spread: Swelling in the TMJ can extend to surrounding tissues, affecting the ear.
- Muscle Overlap: The muscles controlling the jaw are closely linked to those around the ear, so tension or spasms can result in ear discomfort.
- Nerve Pathways: Shared nerve pathways between the jaw and ear mean pain can radiate, causing earaches.
What Are the Common Symptoms Linking TMJ Disorders to Ear Issues? 🔍
Individuals with TMD might experience:
- Ear Pain or Fullness: A sensation of aching or pressure in the ear without infection.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sounds in the ear.
- Hearing Difficulties: Muffled hearing or slight hearing loss.
- Jaw Symptoms: Pain, clicking, or locking of the jaw.
How Is TMJ-Related Ear Pain Diagnosed? 🩺
Diagnosis involves:
- Medical History Review: Discussing symptoms and potential triggers.
- Physical Examination: Assessing jaw movement, listening for joint sounds, and checking for areas of tenderness.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to visualize joint structure.
What Are the Treatment Options for TMJ-Related Ear Pain? 💊
Effective treatments include:
- Self-Care Practices:
- Dietary Modifications: Opt for soft foods to minimize jaw strain.
- Jaw Exercises: Gentle stretching to improve mobility.
- Stress Management: Techniques like meditation to reduce clenching.
- Medications:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen.
- Muscle Relaxants: To alleviate muscle tension.
- Therapies:
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and modalities.
- Dental Appliances: Mouthguards to prevent teeth grinding.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Arthrocentesis: Minimally invasive joint lavage.
- Open-Joint Surgery: For severe cases unresponsive to other treatments.
Conclusion 🌟
The close proximity of the temporomandibular joint to the ear means that TMJ disorders can often manifest as ear pain. Recognizing this connection is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. If you’re experiencing unexplained ear discomfort alongside jaw issues, consulting with a healthcare professional can pave the way to relief.
FAQ ❓
1. Can TMJ disorders cause ear infections?
No, while TMJ disorders can cause ear pain, they don’t lead to ear infections.
2. Is tinnitus from TMJ permanent?
Not necessarily; addressing the TMJ disorder often alleviates tinnitus symptoms.
3. Can stress worsen TMJ-related ear pain?
Yes, stress can lead to jaw clenching, exacerbating TMJ symptoms.
4. Are there home remedies for TMJ-related ear pain?
Applying warm compresses and practicing relaxation techniques can provide relief.
5. How long does TMJ-related ear pain last?
Duration varies; with appropriate treatment, symptoms can improve within weeks.
6. Can poor posture contribute to TMJ disorders?
Yes, poor posture can strain jaw muscles, potentially leading to TMJ issues.
7. Is surgery always required for TMJ disorders?
No, most cases are managed with non-surgical treatments.
References:
- TMJ and Ear Pain – Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
- TMJ disorders – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
- How TMD Affects the Ears – Staten Island Dentists











Post Comment