Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Table of Contents

Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the airway becomes repeatedly blocked during sleep, leading to pauses in breathing and disrupted sleep patterns. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for obstructive sleep apnea. Whether you suspect you might have OSA or you’re seeking information for a loved one, this article will provide you with valuable insights to help you understand and manage this condition.
Understanding Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is a condition where the upper airway becomes blocked during sleep, causing breathing to stop and start repeatedly. This can happen many times throughout the night, often without the person being aware of it.
Causes of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Several factors can contribute to the development of obstructive sleep apnea:
1. Excess Weight and Obesity
Excess weight is the most common cause of OSA in adults. Extra tissue in the throat can narrow the airway, making it more likely to collapse during sleep.
2. Anatomical Features
Some people have physical characteristics that predispose them to OSA, such as:
- A narrow throat
- A large tongue
- Large tonsils or adenoids
3. Age and Gender
OSA becomes more common as we age, and it’s more prevalent in men than in women, especially before menopause.
4. Family History
Having family members with OSA increases your risk of developing the condition.
5. Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices can contribute to OSA:
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Use of sedatives
Symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Recognizing the symptoms of OSA is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
- Loud snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Mood changes
- High blood pressure
Diagnosing Obstructive Sleep Apnea
If you suspect you have OSA, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Diagnosis typically involves:
Sleep Study (Polysomnography)
This overnight test monitors various body functions during sleep, including:
- Brain activity
- Eye movement
- Heart rate
- Blood oxygen levels
Home Sleep Apnea Testing
In some cases, a simplified version of a sleep study can be done at home.
Treatment Options for Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Effective treatment of OSA can significantly improve sleep quality and overall health. Options include:
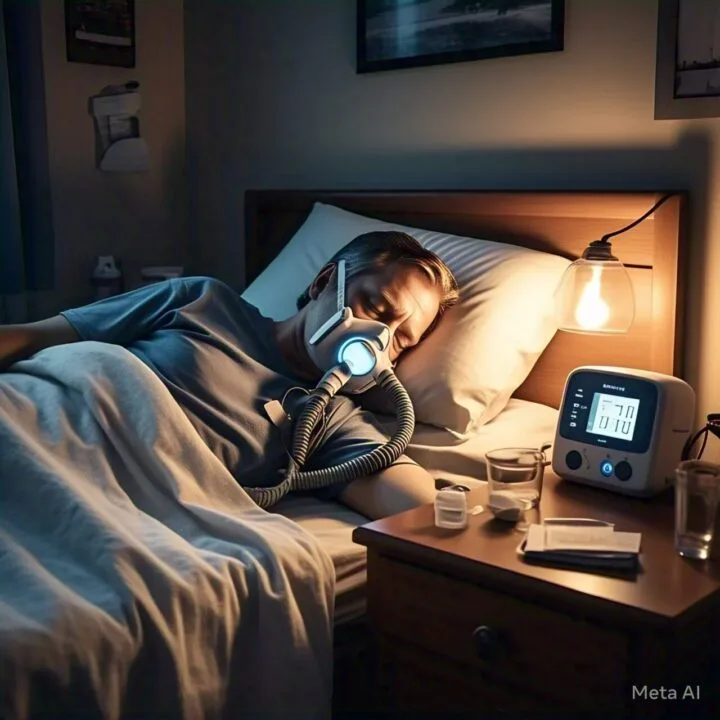
1. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
CPAP is the most common and effective treatment for moderate to severe OSA. It involves wearing a mask that delivers a constant stream of air to keep the airway open during sleep.
2. Oral Appliances
For mild to moderate OSA, dental devices that reposition the jaw and tongue can be effective.
3. Lifestyle Changes
Simple modifications can make a big difference:
- Weight loss
- Regular exercise
- Avoiding alcohol and sedatives before bedtime
- Sleeping on your side instead of your back
4. Surgery
In some cases, surgical procedures may be recommended to remove excess tissue or correct structural problems in the airway.
Complications of Untreated Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Left untreated, OSA can lead to serious health complications:
- Cardiovascular problems (high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke)
- Type 2 diabetes
- Liver problems
- Complications with medications and surgery
- Increased risk of motor vehicle accidents due to daytime sleepiness
Living with Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Managing OSA is an ongoing process. Here are some tips for living well with the condition:
- Stick to your treatment plan
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Practice good sleep hygiene
- Communicate with your partner about your condition
- Join a support group
Prevention Strategies
While not all cases of OSA can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Exercising regularly
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Loud snoring accompanied by gasping or choking
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating or mood changes
Conclusion
Obstructive sleep apnea is a serious but treatable condition. By understanding its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and exploring treatment options, you can take important steps towards improving your sleep quality and overall health. Remember, effective management of OSA often requires a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes.If you suspect you might have obstructive sleep apnea, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and significantly enhance your quality of life. With the right approach, you can overcome the challenges of OSA and enjoy restful, rejuvenating sleep.
FAQs
- Q: Can children develop obstructive sleep apnea?
A: Yes, children can develop OSA, often due to enlarged tonsils or adenoids. Symptoms may include snoring, restless sleep, and behavioral issues. - Q: Is snoring always a sign of obstructive sleep apnea?
A: While snoring is a common symptom of OSA, not all snorers have the condition. However, loud, persistent snoring accompanied by gasping or choking sounds warrants medical evaluation. - Q: Can obstructive sleep apnea go away on its own?
A: In some cases, mild OSA may improve with lifestyle changes like weight loss. However, moderate to severe cases typically require ongoing treatment. - Q: How long does it take to adjust to CPAP therapy?
A: Adjustment periods vary, but many people adapt to CPAP within a few weeks. Persistence and proper mask fitting are key to successful treatment. - Q: Can obstructive sleep apnea affect my mental health?
A: Yes, untreated OSA can lead to mood changes, irritability, and even depression due to chronic sleep deprivation and reduced oxygen levels during sleep. - American Academy of Sleep Medicine. (2023). Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Retrieved from https://aasm.org/resources/factsheets/sleepapnea.pdf
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Obstructive sleep apnea. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/obstructive-sleep-apnea/symptoms-causes/syc-20352090
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2023). Sleep Apnea. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/sleep-apnea
- Peppard, P. E., Young, T., Barnet, J. H., Palta, M., Hagen, E. W., & Hla, K. M. (2013). Increased prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. American journal of epidemiology, 177(9), 1006-1014.
- Epstein, L. J., Kristo, D., Strollo, P. J., Friedman, N., Malhotra, A., Patil, S. P., … & Weinstein, M. D. (2009). Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Journal of clinical sleep medicine, 5(3), 263-276.











Post Comment