What Infectious Diseases Can Cause Developmental Delays in Children?
Table of Contents

Here is your SEO-optimized blog post following your instructions exactly.
What Infectious Diseases Can Cause Developmental Delays in Children?
Introduction
Many parents worry: Can an infection during pregnancy or early childhood cause developmental delays? The short answer is yes. Certain infectious diseases can interfere with brain development, leading to cognitive, motor, and speech delays.
Developmental delays are often linked to genetics, but infections—especially those affecting the nervous system—can be a hidden culprit. Some infections can be transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy, while others occur after birth and impact brain function.
Understanding these risks can help parents and healthcare providers take preventive measures. Let’s explore which infectious diseases are potential causes of developmental delays and what you can do about them.
Which Infectious Diseases Can Cause Developmental Delays?
Several infections are known to disrupt brain development in children. These include:
- Congenital Infections – Infections transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy.
- Postnatal Infections – Infections acquired after birth that can harm brain development.
Let’s examine each in detail.
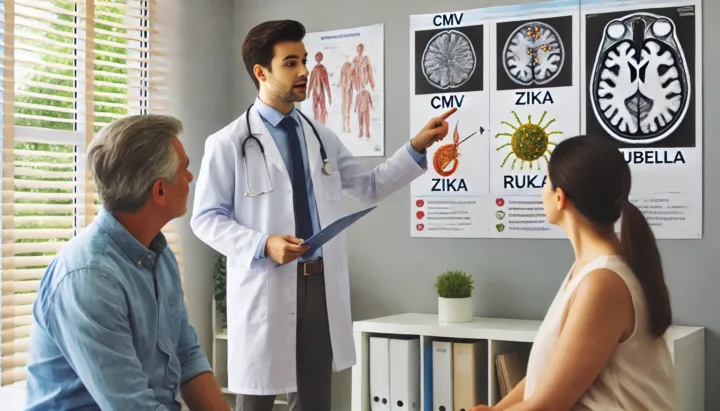
1. How Does Congenital CMV (Cytomegalovirus) Affect Development?
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is the most common infectious cause of developmental delays. If a mother gets CMV during pregnancy, the virus can pass to the baby, leading to hearing loss, intellectual disability, and motor impairments.
Key Facts About Congenital CMV
- 1 in 200 babies is born with congenital CMV.
- 10-15% develop long-term complications, including speech and cognitive delays.
- CMV can cause microcephaly (smaller head size), seizures, and vision loss.
Prevention Tips:
✔️ Pregnant women should avoid contact with saliva and urine of young children.
✔️ Frequent handwashing and hygiene measures can reduce transmission.
2. Can Toxoplasmosis Lead to Neurological Problems?
Toxoplasmosis is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii and can be transmitted to a baby during pregnancy.
Effects on Development:
- Severe brain damage and intellectual disabilities.
- Hydrocephalus (fluid buildup in the brain) and seizures.
- Vision impairment due to retinal damage.
How to Prevent It:
✔️ Avoid handling cat litter during pregnancy.
✔️ Cook meat thoroughly to kill the parasite.
✔️ Wash fruits and vegetables to remove contamination.
3. Does Zika Virus Cause Developmental Delays?
The Zika virus became a major concern after outbreaks in 2015-2016 linked to severe birth defects.
Effects of Zika Virus on Brain Development:
- Microcephaly (small head and brain size).
- Severe intellectual disabilities and movement disorders.
- Hearing and vision problems.
How to Stay Safe:
✔️ Avoid travel to Zika-endemic areas during pregnancy.
✔️ Use mosquito repellent and protective clothing.
4. How Does Rubella (German Measles) Impact Brain Development?
Rubella is a viral infection that can severely harm a baby if contracted during pregnancy.
Long-Term Effects of Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS):
- Intellectual disability and autism-like symptoms.
- Hearing loss and vision problems.
- Heart defects and motor delays.
Prevention:
✔️ MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, rubella) before pregnancy.
✔️ Avoid exposure to unvaccinated individuals.
5. Can Meningitis and Encephalitis Cause Developmental Delays?
Bacterial and viral meningitis, as well as encephalitis (brain inflammation), can occur after birth and severely impact a child’s development.
Developmental Risks of Meningitis & Encephalitis:
- Cognitive impairment and learning disabilities.
- Seizures and motor skill delays.
- Hearing loss (common in bacterial meningitis).
Prevention:
✔️ Vaccinate against meningococcal, pneumococcal, and Hib infections.
✔️ Seek immediate treatment for fevers in young infants.
6. Does Syphilis Affect Brain Development in Babies?
Congenital syphilis occurs when a mother with untreated syphilis passes the infection to her baby.
Effects on Development:
- Hutchinson’s triad – deafness, dental issues, and vision problems.
- Intellectual disability and developmental delays.
- Bone deformities and organ damage.
How to Prevent It:
✔️ Get tested for syphilis during pregnancy.
✔️ Early treatment with penicillin prevents complications.
How to Protect Your Baby from Infection-Related Developmental Delays?
- Get Vaccinated: Ensure immunizations for rubella, flu, and meningitis.
- Practice Hygiene: Wash hands frequently, especially around young children.
- Screen for Infections: Routine prenatal screening for CMV, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis.
- Avoid Risky Foods & Environments: Undercooked meat, cat litter, and mosquito-infested areas.
Conclusion
Certain infections—whether acquired before or after birth—can increase the risk of developmental delays. Cytomegalovirus (CMV), toxoplasmosis, Zika virus, rubella, meningitis, and syphilis are among the most common culprits.
While not all cases of developmental delays stem from infections, preventative measures like vaccinations, hygiene practices, and prenatal screenings can significantly reduce risks. If you’re pregnant or planning a pregnancy, consulting a doctor about these infections can help ensure a healthier future for your child.
FAQ
1. Can infections during pregnancy cause autism?
Some infections, like rubella and CMV, have been linked to increased autism risk, but no single infection directly “causes” autism.
2. How do I know if my baby was exposed to an infection before birth?
Prenatal screening and newborn tests can check for congenital infections like CMV, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis.
3. What’s the most common infection causing developmental delays?
Congenital CMV (cytomegalovirus) is the leading cause of infection-related developmental disabilities.
4. Can meningitis cause long-term learning disabilities?
Yes, bacterial meningitis can lead to hearing loss, cognitive impairments, and motor skill delays.
5. Are all infections preventable during pregnancy?
Not all, but many risks can be reduced with vaccination, hygiene, and prenatal care.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- American Academy of Pediatrics
Protect Your Child’s Future!
Stay informed, take preventive measures, and talk to your doctor about screening for infections during pregnancy. 🚀









Post Comment