How to Relieve Persistent Ear Pain Caused by Infections, TMJ, or Sinus Issues
Table of Contents
How to Relieve Persistent Ear Pain Caused by Infections, TMJ, or Sinus Issues
Introduction
Persistent ear pain can be a frustrating experience, especially when you’re unsure of its cause. Whether it’s due to an ear infection, jaw problems like TMJ (temporomandibular joint disorder), or sinus congestion, understanding how to relieve persistent ear pain can make a significant difference. This blog explores effective remedies, common causes, and when to seek professional help.
What Are the Common Causes of Persistent Ear Pain?
Persistent ear pain may have several underlying causes, including:
1. Ear Infections (Otitis Media or Swimmer’s Ear)
- Middle ear infections: Common in children and adults, often caused by colds or allergies that lead to fluid buildup behind the eardrum.
- Swimmer’s ear: An external ear infection due to water trapped in the ear canal, causing bacterial growth.
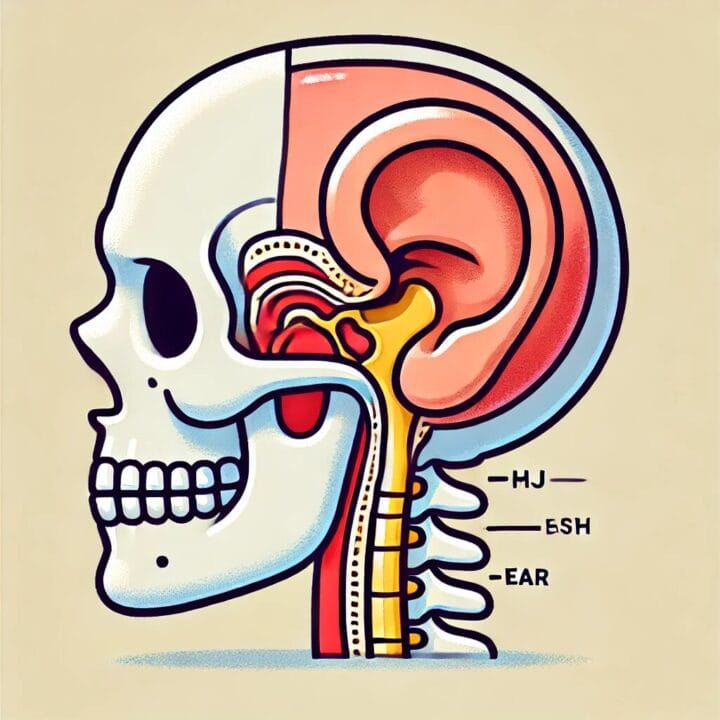
2. TMJ Disorder (Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction)
- TMJ disorder occurs when the jaw joint is inflamed or misaligned, leading to referred pain that often radiates to the ear.
- Symptoms include jaw stiffness, difficulty chewing, and ear pain without an actual ear infection.
3. Sinus Issues or Nasal Congestion
- When the sinuses are blocked, pressure can build up around the ear canal, causing pain or a clogged sensation.
- Sinus infections, colds, and allergies are common triggers.
How to Relieve Persistent Ear Pain at Home
1. Warm Compresses
Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help soothe inflammation and improve circulation, offering relief from pain.
How to do it:
- Soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring it out, and place it gently over the ear for 10-15 minutes.
2. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can reduce pain and inflammation.
Pro Tip: Follow the dosage instructions carefully to avoid side effects.
3. Steam Therapy for Sinus-Related Pain
If sinus congestion is causing your ear pain, steam inhalation can help.
How to do it:
- Boil water, place a towel over your head, and inhale the steam for 5-10 minutes.
4. Hydrogen Peroxide Ear Drops
For cases involving swimmer’s ear or wax buildup, hydrogen peroxide can help.
How to use:
- Put a few drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide in the ear and let it sit for 5 minutes before draining.
5. Gentle Jaw Exercises for TMJ Pain Relief
If the pain is TMJ-related, gentle jaw exercises can improve flexibility and reduce tension.
Try this:
- Slowly open and close your mouth 10-15 times, making sure not to overstretch the jaw.
When Should You See a Doctor for Persistent Ear Pain?
Home remedies are effective for mild to moderate ear pain, but you should seek medical attention if:
- The pain lasts more than 48 hours without improvement.
- You experience hearing loss or discharge from the ear.
- The pain is accompanied by fever, dizziness, or swelling around the ear.
Medical Treatments for Persistent Ear Pain
1. Antibiotics for Bacterial Infections
If your ear pain is due to a bacterial infection, your doctor may prescribe oral or topical antibiotics.
2. Drainage Procedures
In severe cases of fluid buildup, a doctor may recommend draining the ear using a myringotomy.
3. TMJ Therapy
Treatments may include bite guards, physical therapy, or medications to relieve TMJ-induced pain.
Preventing Persistent Ear Pain
- Keep ears dry: Use earplugs while swimming to avoid swimmer’s ear.
- Manage allergies: Take antihistamines if you’re prone to sinus congestion.
- Practice good dental care: TMJ disorders can sometimes be linked to poor dental alignment.
Conclusion
Understanding how to relieve persistent ear pain requires identifying the root cause, whether it’s an infection, TMJ disorder, or sinus issues. While home remedies like warm compresses and steam inhalation can provide temporary relief, persistent or severe cases should be addressed by a healthcare professional. Don’t ignore prolonged ear pain—early intervention can prevent complications and improve your overall comfort.
FAQs About Persistent Ear Pain
1. Can TMJ disorder cause ear pain without any ear infection?
Yes, TMJ dysfunction often leads to referred pain in the ears due to the proximity of the jaw joint to the ear canal.
2. What’s the difference between middle ear infections and swimmer’s ear?
Middle ear infections affect the space behind the eardrum and are typically due to fluid buildup. Swimmer’s ear involves infection of the external ear canal due to trapped water.
3. Can sinus congestion lead to ear pain?
Yes, blocked sinuses can create pressure that affects the ear canal, causing pain or a clogged sensation.
4. How long should I try home remedies before seeing a doctor?
If the pain persists for more than 48 hours or worsens, consult a healthcare provider.
5. Are there any long-term risks associated with untreated ear pain?
Chronic or untreated ear pain can lead to complications such as hearing loss, infections, or TMJ-related jaw problems.
Meta Tags
- Meta Description: Learn how to relieve persistent ear pain caused by infections, TMJ, or sinus issues with effective home remedies and medical treatments.
- Meta Keywords: persistent ear pain relief, ear pain from TMJ, ear pain and sinus congestion, how to relieve ear pain, home remedies for ear pain
- Permalink: how-to-relieve-persistent-ear-pain
- Alt Text for Image: Illustration showing common causes and remedies for persistent ear pain, including TMJ, sinus issues, and ear infections.
Image Prompt
“An informative, clean medical infographic highlighting the causes and remedies for persistent ear pain, showing icons representing TMJ disorder, sinus congestion, and ear infections with soothing color tones.”
Suggested Keywords
- Persistent ear pain relief
- TMJ ear pain remedies
- Causes of ear pain from sinus congestion
- Ear pain and middle ear infections
- Home treatments for swimmer’s ear
- Chronic ear pain symptoms
- Over-the-counter remedies for ear pain
- Warm compress benefits for ear pain
- How TMJ affects the ear
- Ear pain and jaw stiffness connection











Post Comment