Anxiety and Chest Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Find Relief
Table of Contents
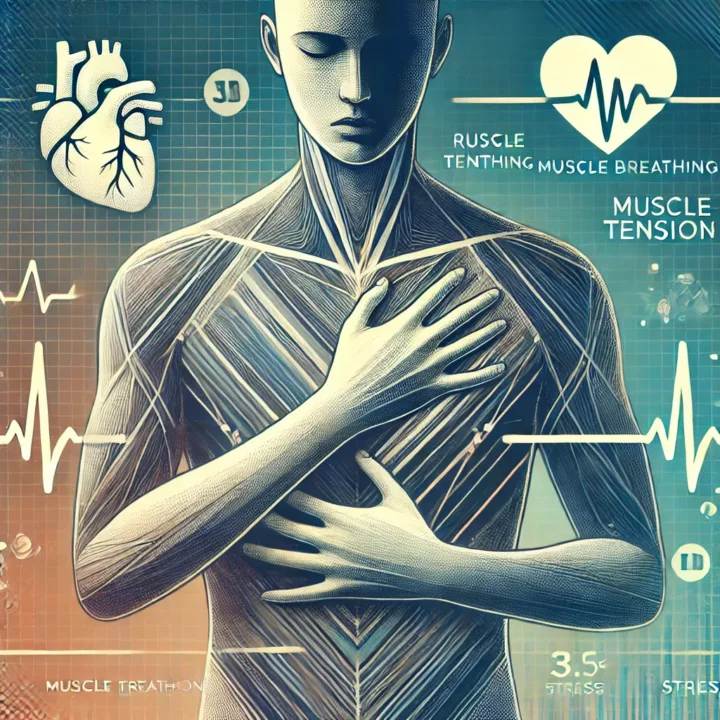
Anxiety and Chest Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and How to Find Relief
Introduction
Have you ever felt a sudden pain or tightness in your chest during moments of anxiety and wondered, “Is this serious, or is it just anxiety?” Chest pain is one of the most alarming symptoms of anxiety, often mimicking heart-related issues and leaving sufferers in a state of panic.
The good news is that anxiety-related chest pain is usually harmless, though it can feel very real and frightening. Understanding the difference between anxiety-induced chest pain and heart-related chest pain is key to managing your symptoms and finding relief.
In this blog, we’ll explore why anxiety can cause chest pain, how to differentiate it from heart problems, and practical steps you can take to reduce anxiety and chest discomfort.
Why Does Anxiety Cause Chest Pain?
When you experience anxiety or panic, your body activates its “fight-or-flight” response. This response triggers the release of adrenaline and other stress hormones, leading to physical changes such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and muscle tension. These changes can cause or worsen chest pain in several ways:
1. Muscle Tension
Anxiety causes the muscles in the chest to tighten, leading to pain, discomfort, or a sensation of heaviness.
2. Hyperventilation
Rapid, shallow breathing (hyperventilation) during a panic attack can reduce carbon dioxide levels in the blood, leading to chest pain, dizziness, and tingling sensations.
3. Increased Heart Rate (Palpitations)
Anxiety-induced palpitations can cause chest discomfort or a pounding sensation, especially if the heart is working harder than normal.
4. Gastroesophageal Reflux (GERD)
Anxiety can trigger acid reflux, which may cause burning chest pain that mimics heart-related pain.
What Does Anxiety-Related Chest Pain Feel Like?
Anxiety-related chest pain can vary from person to person but often includes the following sensations:
- Tightness or pressure across the chest
- Sharp, stabbing pain on one side of the chest
- A burning or aching sensation
- Fluttering or palpitations
- Pain that worsens with stress but eases during relaxation
Duration:
Anxiety chest pain usually lasts for a few minutes to an hour and often subsides once the anxiety or panic attack passes.
How to Differentiate Anxiety Chest Pain from Heart Problems
Although anxiety-related chest pain is typically harmless, it’s important to distinguish it from cardiac chest pain. If you’re unsure, always seek medical advice to rule out serious conditions.
Key Differences Between Anxiety and Cardiac Chest Pain:
| Feature | Anxiety Chest Pain | Cardiac Chest Pain |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden, often triggered by stress or panic | Gradual or sudden, often triggered by exertion |
| Location | Usually sharp or localized to one side | Central, spreading to arms, shoulders, or jaw |
| Duration | Typically short (a few minutes to an hour) | Can last longer, especially during physical activity |
| Relief | Improves with relaxation or controlled breathing | May not improve with rest and often requires medical intervention |
| Associated Symptoms | Rapid breathing, dizziness, sweating, tingling | Nausea, shortness of breath, cold sweats |
If you experience severe, persistent chest pain or pain accompanied by symptoms like shortness of breath or fainting, seek immediate medical attention.
Common Triggers of Anxiety-Related Chest Pain
Understanding what triggers your anxiety and chest pain can help you avoid or manage future episodes. Common triggers include:
- High-stress situations (work deadlines, public speaking)
- Panic attacks or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Caffeine or stimulant overuse
- Lack of sleep
- Financial or personal conflicts
Effective Ways to Relieve Anxiety-Related Chest Pain
1. Practice Deep Breathing Exercises
Slow, controlled breathing can help reduce hyperventilation and muscle tension, easing chest pain.
- How to do it:
- Inhale through your nose for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 4 seconds.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for 6 seconds.
- Repeat until you feel calmer.
2. Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Tension in the chest muscles can worsen pain, so releasing that tension is essential. Progressive muscle relaxation involves tensing and relaxing different muscle groups to promote physical relaxation.
3. Engage in Mindfulness or Meditation
Mindfulness meditation helps you focus on the present moment, reducing anxiety and its physical symptoms.
- Apps like Calm or Headspace can guide you through effective mindfulness practices.
4. Limit Caffeine and Stimulants
Caffeine can exacerbate anxiety and heart palpitations, contributing to chest pain. Reduce your intake of coffee, tea, and energy drinks.
5. Stay Physically Active
Regular exercise reduces overall anxiety levels and improves cardiovascular health, reducing the frequency of anxiety-related chest pain.
6. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT can help identify and change negative thought patterns that contribute to anxiety. A mental health professional can help you develop coping strategies.
7. Grounding Techniques During Panic Attacks
Grounding techniques, such as focusing on your surroundings or performing the 5-4-3-2-1 exercise (identifying things you can see, hear, touch, etc.), can help bring you back to the present moment and alleviate anxiety symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Help
Although anxiety-related chest pain is generally not dangerous, you should seek medical advice if:
- The chest pain is severe or persistent
- You experience shortness of breath, nausea, or fainting
- You have a history of heart disease or risk factors such as high blood pressure
It’s always better to be cautious and rule out any serious conditions.
Preventing Future Episodes of Anxiety and Chest Pain
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Poor sleep can worsen anxiety symptoms.
- Incorporate regular exercise: Physical activity helps regulate stress hormones and improve mood.
- Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Journaling, breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help you manage anxiety effectively.
- Reduce triggers: Identify specific anxiety triggers and work to reduce or eliminate them where possible.
Conclusion
Anxiety-related chest pain can feel overwhelming, but it’s important to remember that it is usually harmless and temporary. By understanding the connection between anxiety and chest pain, recognizing the symptoms, and using effective coping strategies, you can manage and reduce these episodes over time. If you’re ever in doubt, seeking medical advice will help you find peace of mind and rule out any underlying health issues.
FAQ
1. How long does anxiety-related chest pain last?
Anxiety chest pain typically lasts a few minutes to an hour and improves once the anxiety subsides.
2. Can anxiety chest pain happen without a panic attack?
Yes, generalized anxiety can cause chest pain even without a full-blown panic attack.
3. How do I know if my chest pain is serious?
If your chest pain is accompanied by shortness of breath, fainting, or pain spreading to the arms or jaw, seek immediate medical attention.
4. Can exercise help reduce anxiety chest pain?
Yes, regular physical activity helps reduce overall anxiety levels and improves cardiovascular health.
5. What medications can help with anxiety-related chest pain?
In some cases, doctors may prescribe anti-anxiety medications or beta-blockers to help manage symptoms. Always consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication.










Post Comment