Why Does My Skin Itch at Night and How Can I Stop It?
Table of Contents
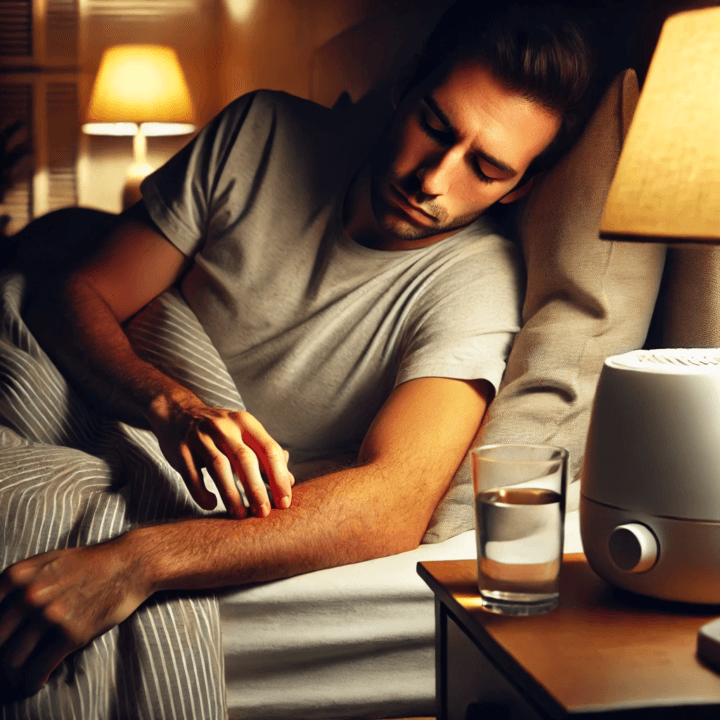

Why Does My Skin Itch at Night and How Can I Stop It?
Introduction
Have you ever found yourself tossing and turning at night, unable to sleep because of relentless itching? You’re not alone. Itchy skin at night, also known as nocturnal pruritus, is a common yet frustrating condition that can ruin your sleep. Whether it’s due to dry skin, an allergic reaction, or an underlying health condition, the constant urge to scratch can make bedtime feel like a battle. But why does this happen, and more importantly, how can you stop it? Keep reading to find out what’s causing your nighttime itching and what you can do to get relief.
What Causes Itchy Skin at Night?
1. Natural Circadian Rhythms and Skin Changes
Your body follows a 24-hour cycle known as the circadian rhythm. At night, changes in hormone levels, like a drop in cortisol, can make your skin more sensitive and prone to itching. Additionally, your body’s temperature rises at night, which can exacerbate skin irritation.
2. Dry Skin (Xerosis)
One of the most common culprits of nighttime itching is dry skin. Without enough moisture, your skin loses its protective barrier, leading to irritation. Factors that can worsen dryness include:
- Low humidity levels
- Overuse of harsh soaps
- Hot showers before bed
3. Skin Conditions (Eczema, Psoriasis, and More)
If you suffer from eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis, you may notice that itching worsens at night. Inflammatory skin conditions often flare up due to reduced hydration and exposure to irritants throughout the day.
4. Allergic Reactions and Irritants
Certain fabrics, laundry detergents, and even skincare products can trigger allergic reactions that lead to itching. Common irritants include:
- Synthetic fabrics (like polyester)
- Fragranced lotions or body washes
- Dust mites and pet dander
5. Bed Bugs or Insect Bites
Waking up with itchy welts? It might not be your imagination—bed bugs, mosquitoes, or mites can cause itching that intensifies at night. If you notice small red bites in clusters, inspect your mattress and bedding for signs of infestation.
6. Underlying Medical Conditions
Sometimes, persistent itching can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition such as:
- Liver disease – High bile salt levels in the blood can cause severe itching.
- Kidney disease – Toxin buildup can lead to pruritus.
- Diabetes – Nerve damage and dry skin contribute to itching.
- Thyroid disorders – Hormonal imbalances can dry out the skin and cause irritation.
How Can You Stop Itchy Skin at Night?
1. Moisturize Before Bed
Using a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer before bed can help lock in moisture and soothe dry skin. Look for ingredients like:
- Ceramides – Strengthen the skin barrier
- Hyaluronic acid – Hydrates deeply
- Colloidal oatmeal – Soothes inflammation
2. Use a Humidifier
Dry air can worsen itching, especially during colder months. A humidifier helps maintain skin hydration by adding moisture to the air in your bedroom.
3. Switch to Gentle Skincare and Fabrics
If your itching is triggered by allergens or irritants, consider making these changes:
- Use hypoallergenic, fragrance-free lotions and soaps
- Wash clothes with dye-free, fragrance-free detergent
- Wear breathable, cotton or bamboo pajamas
4. Take a Lukewarm Bath with Oatmeal or Baking Soda
Soaking in an oatmeal or baking soda bath can relieve itchy skin. Colloidal oatmeal has anti-inflammatory properties, while baking soda balances the skin’s pH.
5. Keep Your Room Cool and Comfortable
Overheating can make itching worse. Keep your bedroom temperature around 65-70°F (18-21°C) and use lightweight bedding.
6. Try Over-the-Counter Anti-Itch Creams
If itching is persistent, topical treatments can provide relief. Some options include:
- Hydrocortisone cream – Reduces inflammation
- Calamine lotion – Soothes irritation
- Antihistamine creams – Helps with allergic reactions
7. Take an Antihistamine Before Bed
If your itching is due to allergies, taking an oral antihistamine like Benadryl (diphenhydramine) before bed can help reduce symptoms and promote sleep.
8. Address Underlying Health Conditions
If your itching persists despite trying these remedies, consult a doctor to rule out underlying conditions such as liver or kidney disease. Blood tests may be needed to check for internal causes.
Conclusion
Nighttime itching can be a frustrating and uncomfortable experience, but it is often treatable with the right approach. Whether it’s using a moisturizer, switching to hypoallergenic bedding, or addressing an underlying medical condition, you don’t have to suffer through sleepless nights anymore. If your symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare provider is the best step to find lasting relief.
FAQ
1. Why does my skin only itch at night?
Your body undergoes hormonal and temperature changes at night, which can make your skin more sensitive. Additionally, distractions are minimal, making you more aware of the itching.
2. Can stress cause itchy skin at night?
Yes. Stress triggers the release of inflammatory chemicals that can cause or worsen itching, especially in conditions like eczema and psoriasis.
3. How can I stop scratching at night?
Try keeping your nails short, wearing gloves while sleeping, or applying a cold compress to the itchy area before bed.
4. Is nighttime itching a sign of something serious?
It can be. If your itching is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other symptoms like weight loss or jaundice, consult a doctor to rule out serious conditions.
5. Does drinking more water help with itchy skin?
Yes! Hydrated skin is less likely to become dry and irritated. Drinking enough water and using a good moisturizer can significantly reduce itching.












Post Comment