What Causes Excessive Heat and How Can You Stay Cool?
Table of Contents
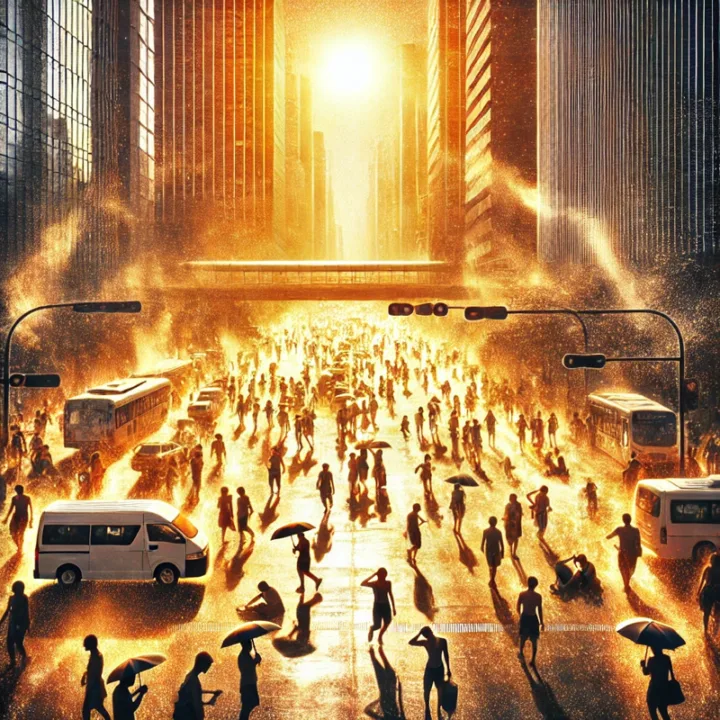

Introduction
As temperatures surge worldwide, excessive heat has become more than just an inconvenience—it’s a significant health hazard. You may be wondering: Why does it get so unbearably hot, and how can we protect ourselves? With record-breaking heat waves sweeping across continents, many are searching for answers to combat the blistering temperatures. Understanding the root causes of excessive heat and how to stay cool is crucial for your health and well-being. Whether you’re trying to survive a heatwave in the city or planning your daily outdoor routine, this guide has you covered.
By the end of this article, you’ll know the common triggers of extreme heat, why it’s getting worse, and actionable steps you can take to stay safe when the heat rises.
What Causes Excessive Heat Events?
1. How Does Climate Change Contribute to Rising Temperatures?
Climate change is a major driver of extreme heat events. Global warming caused by the greenhouse effect traps heat within the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to an overall rise in temperatures.
Key contributors include:
- Burning of fossil fuels: Emissions from cars, power plants, and factories release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
- Deforestation: Forests act as natural coolers by absorbing carbon dioxide. Without them, the planet retains more heat.
- Urban heat islands: Cities with concrete buildings, asphalt roads, and limited greenery tend to be significantly warmer than rural areas.
Did you know? The average global temperature has risen by about 1.1°C since the pre-industrial era, with cities experiencing even more dramatic changes.
2. What Natural Phenomena Lead to Extreme Heat?
Certain weather patterns also trigger excessive heat events. Some of the key factors include:
- Heat domes: When a high-pressure system traps warm air over a region, it causes prolonged heatwaves.
- El Niño: This climate pattern warms the Pacific Ocean, affecting global weather and leading to hotter-than-average conditions.
- Droughts: Lack of rain means less moisture in the air, which amplifies heat.
What Are the Dangers of Excessive Heat?
Excessive heat isn’t just uncomfortable—it can be life-threatening.
1. How Does Extreme Heat Affect Your Body?
When your body overheats, it struggles to cool down, leading to dehydration and heat-related illnesses. The most common conditions include:
- Heat cramps: Painful muscle spasms due to electrolyte imbalances.
- Heat exhaustion: Symptoms like heavy sweating, dizziness, and nausea.
- Heatstroke: A medical emergency where body temperature exceeds 104°F (40°C), leading to organ damage.
2. Who Is Most at Risk?
- Elderly individuals: Aging reduces the body’s ability to regulate temperature.
- Children: They produce more heat during physical activity and have limited sweating capacity.
- People with chronic illnesses: Conditions like diabetes or heart disease increase vulnerability.
- Outdoor workers: Construction workers, farmers, and others exposed to prolonged heat.
How Can You Stay Safe During Extreme Heat?
1. What Should You Wear in Hot Weather?
- Loose, light-colored clothing: Reflects heat rather than absorbing it.
- Breathable fabrics: Cotton and linen allow airflow, keeping your body cool.
- Wide-brim hats: Protect your head and face from direct sunlight.
2. How Much Water Should You Drink?
Staying hydrated is your first line of defense. Experts recommend:
- 2-3 liters of water per day on average.
- Electrolyte-rich drinks during prolonged physical activity or when sweating heavily.
- Avoiding alcohol and caffeine, which dehydrate the body.
3. How Can You Cool Down Your Home?
- Close blinds and curtains during the hottest part of the day.
- Use fans or air conditioning to circulate cool air.
- Create cross-ventilation by opening windows on opposite sides of the house.
Why Is Excessive Heat Becoming More Common?
1. Is Climate Change the Main Culprit?
Yes, climate change plays a pivotal role, but it’s not the only factor.
- Urbanization: Rapid growth in cities leads to heat-retaining infrastructures.
- Population growth: More people require more energy, contributing to emissions.
- Deforestation: Removing trees reduces natural cooling mechanisms.
2. How Do Human Activities Worsen Heat Events?
Human activities such as over-reliance on fossil fuels and inefficient cooling systems increase both indoor and outdoor temperatures. In fact, energy demand spikes during heatwaves, further straining power grids and increasing emissions.
What Are Long-Term Solutions for Managing Heat?
1. Can Green Spaces Help Reduce Urban Heat?
Yes, introducing more parks, trees, and rooftop gardens can make cities cooler by providing shade and increasing moisture in the air.
2. How Can Sustainable Building Design Reduce Heat?
Green buildings equipped with reflective roofs, proper insulation, and natural ventilation can maintain cooler indoor environments.
- Passive cooling: Designing homes with shaded windows and high ceilings to improve air circulation.
- Energy-efficient air conditioners: Reduce overall heat production.
3. What Role Do Governments and Communities Play?
- Heat action plans: Many cities have introduced early warning systems and cooling centers.
- Public education: Teaching citizens how to stay safe during heatwaves.
- Investment in renewable energy: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Excessive heat is a growing problem, but with the right strategies, you can protect yourself and your loved ones. From staying hydrated and wearing the right clothes to understanding the broader impact of climate change, knowledge is your best defense. As cities continue to warm, adopting long-term solutions such as green infrastructure and sustainable living can help mitigate the risks.
Remember: when temperatures spike, your health should be your top priority. Stay informed, stay safe, and stay cool.
FAQ
1. How hot does it have to be to cause heatstroke?
Heatstroke can occur when the body temperature exceeds 104°F (40°C), typically during prolonged exposure to extreme heat or vigorous activity.
2. What’s the difference between heat exhaustion and heatstroke?
Heat exhaustion involves symptoms like heavy sweating and dizziness, while heatstroke is more severe and can lead to organ failure if untreated.
3. Are fans effective in extreme heat?
Fans can help, but when temperatures exceed 95°F (35°C), they may circulate hot air. It’s best to combine fans with other cooling methods.
4. Can excessive heat damage electronics?
Yes, extreme temperatures can cause overheating in devices, leading to reduced performance or permanent damage.
5. How do I know if my home is adequately ventilated?
Signs of poor ventilation include lingering humidity, stale odors, and difficulty cooling rooms. Installing exhaust fans and creating cross-ventilation can help.
Meta Information
Keywords: excessive heat, heat waves, heat exhaustion prevention, stay cool in heat, climate change impact, heat safety tips
Meta Description: Learn about the causes of excessive heat, its dangers, and practical tips for staying cool during heatwaves. Stay safe and informed with our comprehensive guide.
Permalink: /what-causes-excessive-heat-how-to-stay-cool
Alt Text for Featured Image: Scorching city landscape under heatwave conditions, illustrating excessive heat.











Post Comment