Which Foods Should You Avoid to Prevent Skin Inflammation?
Table of Contents

Which Foods Should You Avoid to Prevent Skin Inflammation?
Introduction
Are you tired of dealing with stubborn skin inflammation and wondering if your diet could be the cause? Skin inflammation, whether from acne, eczema, or psoriasis, is often exacerbated by the foods we eat. The primary keyword, “foods to avoid for skin inflammation,” holds the key to understanding which dietary habits might be triggering those flare-ups. Let’s dive deep into how food plays a role in skin health and why eliminating certain items could transform your skin.
Most people think skincare is all about the products you apply. But what if I told you that what’s on your plate matters just as much—if not more? Many common foods, even the ones we consider healthy, can act as silent triggers for skin irritation, redness, and flare-ups. The good news? By identifying these culprits, you can create a diet plan that supports healthy, glowing skin and minimizes inflammation.
In this article, we’ll break down the foods you should avoid, why they cause inflammation, and offer alternatives for a healthier diet.
What Is Skin Inflammation, and How Does Food Impact It?
Skin inflammation refers to redness, swelling, and irritation caused by immune responses to internal or external triggers. From mild acne to severe eczema, inflammation can manifest in different forms, and one major trigger is our diet.
Here’s how certain foods contribute to inflammation:
- Excess sugar: High sugar intake can cause a spike in insulin levels, leading to increased oil production and inflammatory responses.
- Processed foods: They often contain refined carbs, trans fats, and artificial additives that trigger systemic inflammation.
- Dairy products: For many, dairy causes hormonal imbalances, leading to clogged pores and inflammatory skin conditions.
By understanding the role food plays, we gain the power to control inflammation from the inside out.
Which Foods Should You Cut Out Immediately to Improve Skin Health?
1. Refined Sugar and Sweets
- Why it triggers inflammation: Sugar causes spikes in insulin, leading to glycation—a process that damages collagen and accelerates skin aging.
- Hidden culprits: Sodas, candy, baked goods, and even so-called “healthy” fruit juices.
Tip: Switch to natural sweeteners like honey or stevia.
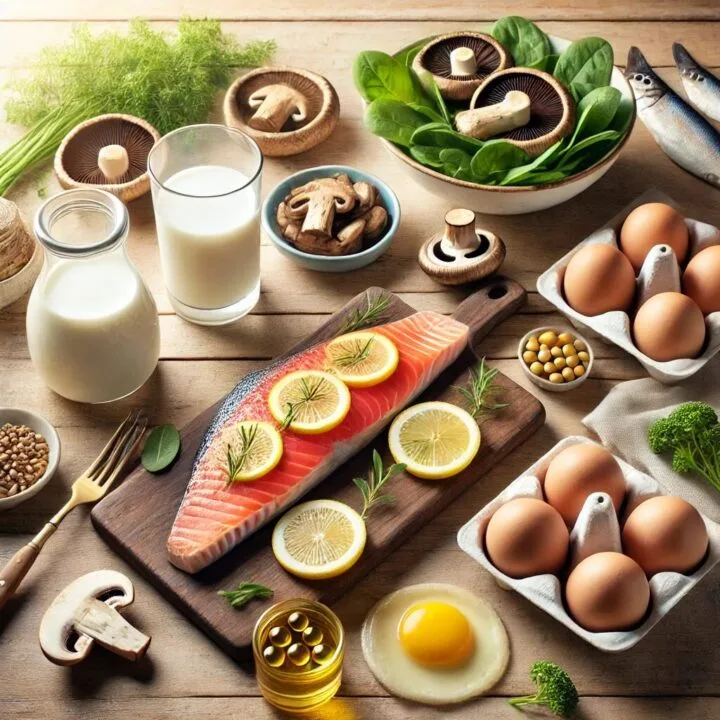
2. Dairy Products
- The problem: Dairy triggers excess sebum production and hormonal fluctuations, causing acne and inflammation.
- Common offenders: Milk, cheese, yogurt, and ice cream.
Alternatives: Almond milk, coconut yogurt, and plant-based cheeses.
3. Processed and Fast Foods
- What’s wrong? Processed foods contain trans fats, preservatives, and refined sugars—all contributing to inflammation.
- Examples: Burgers, fries, chips, and frozen meals.
Tip: Opt for whole, minimally processed foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
4. Gluten and Refined Carbohydrates
- Why they’re inflammatory: Refined carbs spike blood sugar levels, promoting inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Hidden in: White bread, pasta, pastries, and many packaged snacks.
Alternative grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and buckwheat.
5. Alcohol
- How it affects skin: Alcohol dehydrates the body and impairs liver function, making it harder for your body to detoxify and fight inflammation.
- Worst offenders: Beer, cocktails, and sugary wines.
Better choices: Herbal teas, infused water, or mocktails.
6. Fried and Oily Foods
- What happens to your skin: Excessive consumption of fried foods leads to clogged pores and oxidative damage, which worsens inflammation.
- Avoid these: Fried chicken, donuts, onion rings, and potato chips.
Switch to: Air-fried or baked alternatives with healthy oils like olive oil.
7. Artificial Additives and Preservatives
- Why they’re bad: Artificial additives disrupt gut health, which can lead to skin inflammation through the gut-skin axis.
- Hidden sources: Packaged snacks, canned soups, and flavored chips.
Solution: Stick to clean-label products with minimal ingredients.
How Does Gut Health Link to Skin Inflammation?
The gut-skin axis plays a critical role in inflammation. Poor gut health, often due to a diet rich in inflammatory foods, can lead to “leaky gut syndrome,” where toxins enter the bloodstream and cause skin reactions.
Ways to support your gut and reduce inflammation:
- Include probiotics (like yogurt alternatives or fermented foods).
- Eat prebiotic-rich foods such as bananas, garlic, and onions.
- Avoid processed foods that damage gut bacteria.
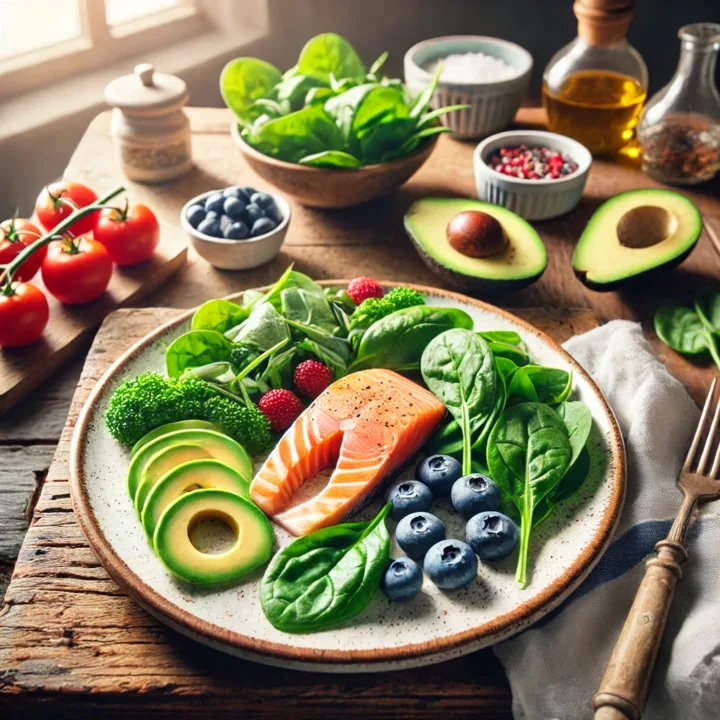
What Are Anti-Inflammatory Foods You Can Eat Instead?
Once you’ve eliminated the triggers, it’s time to focus on skin-friendly foods like:
- Fatty fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids that combat inflammation.
- Leafy greens: Spinach and kale help reduce oxidative stress.
- Berries: Antioxidants in blueberries and strawberries protect skin cells.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a powerful anti-inflammatory compound.
These foods don’t just reduce inflammation; they also boost collagen production and hydrate your skin naturally.
Conclusion
Inflammation is often the root cause of many skin problems, from acne to chronic conditions like eczema. By identifying and avoiding key inflammatory foods such as refined sugar, dairy, and processed meals, you can take control of your skin health. But it’s not just about elimination—it’s equally important to fill your diet with nutrient-dense, anti-inflammatory foods that nourish your body from the inside out.
Remember, glowing, healthy skin isn’t just about what you apply on the outside; it’s about making mindful food choices daily. Start today, and watch your skin thank you!
FAQ
1. Does quitting sugar really help with skin inflammation?
Yes, reducing sugar intake helps minimize insulin spikes, glycation, and excess oil production—all of which contribute to inflamed skin.
2. Are all dairy products bad for skin inflammation?
Not for everyone, but many people experience improvements after reducing or eliminating dairy due to its hormonal effects.
3. Can gluten-free diets improve skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis?
For some, avoiding gluten reduces inflammation and improves symptoms, but consult a healthcare professional to see if it applies to you.
4. What is the role of omega-3 fatty acids in reducing skin inflammation?
Omega-3s from fatty fish or supplements help reduce systemic inflammation and protect skin from damage.
5. Is coffee bad for skin inflammation?
Moderate coffee consumption is generally fine, but excessive intake can trigger dehydration and worsen skin conditions.
6. How long does it take for dietary changes to show improvements in skin health?
Typically, you’ll notice changes in 4-6 weeks, depending on the severity of your condition.
7. Should I avoid spicy foods to prevent skin irritation?
Spicy foods can trigger flushing and sensitivity in some individuals, but not everyone will experience inflammation from them.










Post Comment