What’s the Difference Between Latent and Active Tuberculosis?
Table of Contents
What’s the Difference Between Latent and Active Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major health concern globally, but not all cases of TB are the same. Understanding the difference between latent and active tuberculosis is crucial for diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Whether you’re concerned about exposure or just curious, this guide will help you grasp the key distinctions between these two forms of TB.
What Is Tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs but capable of spreading to other parts of the body. Its symptoms and severity vary based on whether a person has latent or active TB.
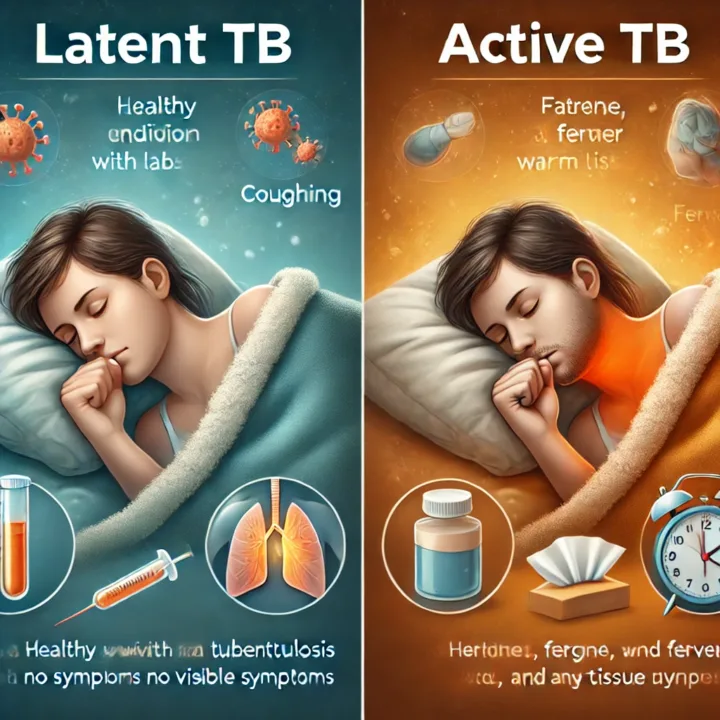
How Does Latent Tuberculosis Differ from Active Tuberculosis?
1. What is Latent Tuberculosis?
Latent tuberculosis occurs when the bacteria remain in the body without causing symptoms. It’s like the infection is “asleep,” meaning the immune system keeps the bacteria under control.
Key Characteristics of Latent TB:
- No symptoms or illness present.
- Not contagious.
- Can become active if the immune system weakens (e.g., due to diabetes, HIV, or malnutrition).
- Detected through a positive TB skin or blood test.
Example: A person exposed to TB bacteria may harbor it for years without ever knowing, only showing signs during immunosuppressive events.
2. What is Active Tuberculosis?
Active tuberculosis happens when the bacteria are no longer controlled by the immune system and begin to multiply, leading to symptoms and potential transmission to others.
Key Characteristics of Active TB:
- Shows symptoms like persistent cough, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
- Contagious, particularly when affecting the lungs.
- Requires immediate treatment to prevent complications and further spread.
What Are the Symptoms of Active Tuberculosis?
Symptoms typically appear gradually but worsen over time. Watch for the following:
- Persistent cough (lasting more than 3 weeks)
- Chest pain or difficulty breathing
- Coughing up blood
- Night sweats
- Fatigue and weakness
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Fever and chills
These symptoms often resemble other diseases, so proper testing is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Can Latent TB Become Active?
Yes, latent tuberculosis can transition into active TB if the body’s immune defenses are compromised. This risk is heightened in individuals with:
- HIV/AIDS
- Diabetes
- Kidney disease
- Certain medications like corticosteroids or chemotherapy
- Poor nutrition or substance abuse
This is why preventive treatment is recommended for those with latent TB who are at high risk of developing active TB.
How Is Tuberculosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis depends on whether the TB is latent or active.
Testing for Latent Tuberculosis
- Tuberculin Skin Test (TST): Involves injecting a small amount of tuberculin into the skin and measuring the reaction.
- Interferon-Gamma Release Assay (IGRA): A blood test to detect TB infection, commonly used for those vaccinated with BCG.
Testing for Active Tuberculosis
- Chest X-ray: To detect lung damage or TB lesions.
- Sputum Test: Analyzes mucus from the lungs for the presence of TB bacteria.
- Blood tests: Help identify bacterial activity in the body.
What Are the Treatment Options?
For Latent TB:
The goal of treatment is to prevent the infection from becoming active. Common medications include:
- Isoniazid (INH) for 6-9 months
- Rifapentine or rifampin in shorter regimens (3-4 months)
For Active TB:
Treatment requires a combination of antibiotics for 6-9 months:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin
- Ethambutol
- Pyrazinamide
Proper adherence to medication is essential to prevent antibiotic resistance, a growing concern with TB.
How Can You Prevent the Spread of Tuberculosis?
Preventive measures focus on limiting exposure and controlling infection:
- For those with active TB: Wear masks, practice good cough hygiene, and complete treatment.
- For those with latent TB: Monitor symptoms regularly and follow preventive treatment if recommended.
- Vaccination: BCG (Bacillus Calmette-Guérin) vaccine provides some protection, especially for children.
What Are the Complications of Untreated TB?
Without treatment, active TB can lead to severe complications, including:
- Lung damage or respiratory failure
- Spread to other organs (extrapulmonary TB)
- Death in severe cases, particularly among immunocompromised individuals
Early detection and treatment are critical in preventing complications and controlling outbreaks.
Conclusion: Why Understanding Latent vs. Active TB Matters
Knowing the difference between latent and active tuberculosis can save lives. While latent TB doesn’t present symptoms or cause immediate harm, it has the potential to become active and contagious. Active TB, on the other hand, demands urgent medical attention to avoid complications and protect others. If you’ve been exposed or suspect infection, seeking medical advice is essential.
FAQ: Common Questions About Latent and Active Tuberculosis
1. Can latent TB go away on its own?
No, latent TB does not disappear without treatment. The bacteria can remain dormant for years, posing a future risk.
2. How long can latent TB remain inactive?
Latent TB can stay dormant for a lifetime or become active anytime the immune system weakens.
3. Is active TB always contagious?
Active TB is contagious when it involves the lungs. Extrapulmonary TB (outside the lungs) may not always spread to others.
4. What are the side effects of TB treatment?
Common side effects include nausea, fatigue, and liver problems. It’s important to consult your doctor if symptoms worsen.
5. Can you get reinfected with TB after treatment?
Yes, it’s possible to get reinfected, especially in high-risk areas or environments.
External Resources for Further Reading
- World Health Organization – Tuberculosis Overview
- CDC – Latent Tuberculosis Information
- Mayo Clinic – Tuberculosis Symptoms and Causes











Post Comment