TMJ Headache Behind Ear Symptoms: What’s Causing Your Pain?
Table of Contents
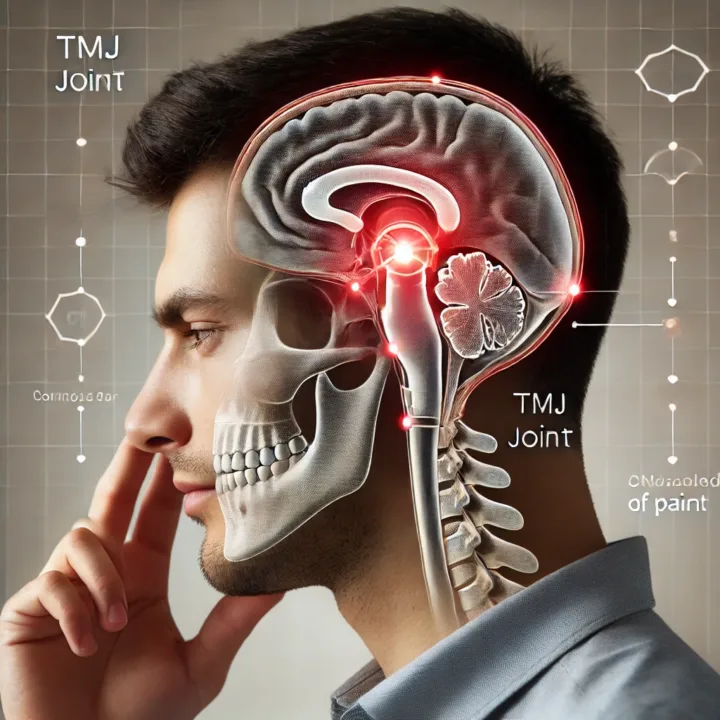
TMJ Headache Behind Ear Symptoms: What’s Causing Your Pain?
Introduction
Are you dealing with a persistent headache that seems to be lurking behind your ear? Is it a throbbing, nagging pain that just won’t quit? You’re not alone. Many people experience what feels like a TMJ headache behind ear symptom, and it can be incredibly frustrating. It might leave you wondering, “Is this just a regular headache? Or is something else going on?” Perhaps you’ve tried over-the-counter pain relievers, but they only provide temporary relief, or maybe you’re starting to suspect that it’s not just a headache but something related to your jaw. The discomfort can even extend to your neck and shoulders, making everyday tasks feel like a struggle.
The good news is, this type of pain often points to an underlying issue with your temporomandibular joint (TMJ), the hinge connecting your jaw to your skull. This joint can be a sneaky culprit, leading to a variety of symptoms that are often misunderstood. The pain from TMJ dysfunction isn’t always straightforward; sometimes it manifests as headaches behind the ear, which can be particularly confusing. Understanding this connection is crucial for finding the right treatment and relief.
What is TMJ?
The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) is a crucial joint that connects the jawbone to the skull, facilitating essential functions such as chewing, talking, and yawning. Any dysfunction of the TMJ, known as temporomandibular disorder (TMD), can result in pain, restricted movement, and discomfort in the surrounding muscles.
Common Causes of TMJ Dysfunction
- Bruxism (Teeth Grinding): Habitual teeth grinding can put excessive pressure on the TMJ, leading to inflammation and pain.
- Jaw Clenching: Stress and anxiety often cause individuals to clench their jaws unknowingly, straining the joint.
- Arthritis: Inflammatory joint conditions such as arthritis can affect the TMJ, causing chronic pain and stiffness.
- Trauma: Direct injury to the jaw or face can result in TMJ dysfunction.
- Malocclusion: Poor dental alignment can put extra stress on the TMJ.
How TMJ Dysfunction Causes Headaches Behind the Ear
The TMJ is located close to the ear, and when it becomes inflamed or misaligned, it can create tension in the surrounding muscles, leading to headaches. The pain may radiate behind the ear, into the temples, or even down into the neck and shoulders.
Common symptoms that may indicate a TMJ-related headache include:
- Pain that worsens with jaw movement.
- Clicking or popping sounds when opening the mouth.
- Ear pain without signs of infection.
- Difficulty chewing or opening the mouth fully.
- Neck and shoulder tension accompanying the headache.
Diagnosing TMJ Headaches
A healthcare provider will typically perform a thorough evaluation that includes:
- Medical History Review: Discussing symptoms, triggers, and previous injuries.
- Physical Examination: Evaluating jaw movement, muscle tenderness, and joint sounds.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to assess joint structure and rule out other conditions.
- Dental Examination: Identifying bite misalignment or bruxism-related damage.
Treatment Options for TMJ Headaches
Conservative Treatments
- Jaw Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises to improve mobility.
- Hot and Cold Therapy: Heat packs can relax tense muscles, while cold packs reduce inflammation.
- Dietary Changes: Soft foods to minimize strain on the jaw.
- Postural Correction: Improving posture to reduce jaw strain.
Medical Interventions
- Medications: NSAIDs, muscle relaxants, or corticosteroids for pain management.
- Mouthguards or Splints: Custom oral appliances to prevent teeth grinding and jaw clenching.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and manual therapy to improve joint function.
- Botox Injections: Used to relax overactive jaw muscles.
- Surgery: In severe cases where conservative treatments fail.
Preventing TMJ Headaches
To minimize the recurrence of TMJ headaches behind the ear, consider the following preventive measures:
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Addressing bite issues and preventing bruxism.
- Avoiding Hard or Chewy Foods: Opt for a soft diet to reduce stress on the TMJ.
- Practicing Good Posture: Proper neck and shoulder alignment can relieve jaw tension.
Conclusion
Understanding the link between TMJ dysfunction and headaches behind the ear is the first step to finding effective relief. Whether through conservative home care or professional treatments, addressing TMJ issues can significantly improve your quality of life.
If you’re experiencing persistent pain, it’s crucial to seek professional help for a comprehensive diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR)
Mayo Clinic









Post Comment